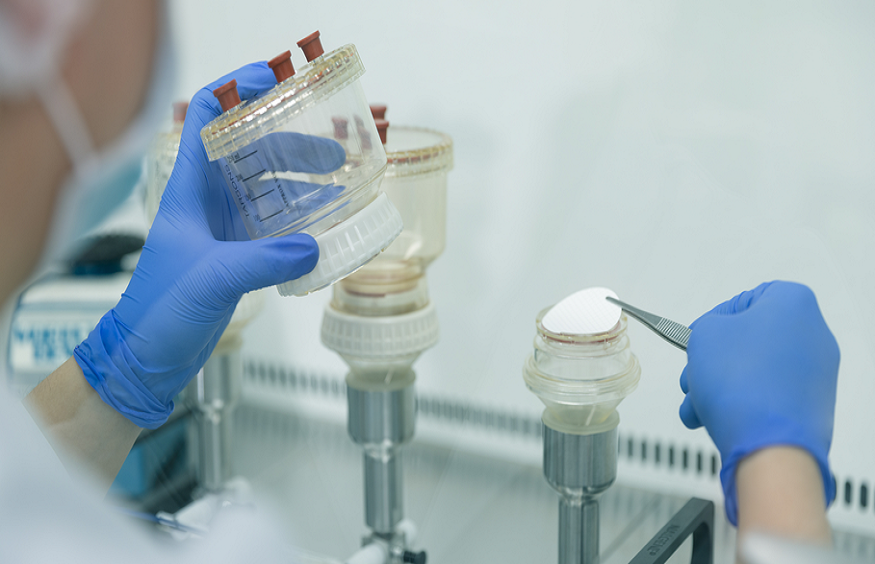
Even products that look immaculate on the surface can still carry hidden contaminants. In industries like medical device manufacturing, maintaining product safety demands rigorous sanitation practices, including bioburden testing. Let’s explore how bioburden testing operates and why it’s so crucial for ensuring product safety and dependability.
Bioburden testing assesses the level of microbial contamination on a product or device before it undergoes sterilization. This test identifies harmful contaminants, such as aerobic and anaerobic bacteria, fungi, and spores, which could compromise the product’s safety.
Precisely measuring bioburden is critical for effective sterilization. Understanding the contamination level allows manufacturers to select a sterilization method that removes harmful microbes without damaging the product itself. Cleanroom testing also plays a key role by ensuring the controlled cleanliness of environments where these items are processed.
The bioburden testing process involves sampling, analyzing to identify and quantify contaminants, and evaluating the results to gauge overall contamination. Techniques like the most probable number (MPN) method may be used to predict microbial presence over time.
An essential part of this testing process is final validation, where the bioburden level is confirmed to verify the sterilization method’s effectiveness and the product’s quality.
For more insights into bioburden testing and its importance in protecting medical devices and other products, you can refer to the provided resource for an in-depth look.